刷题笔记之回溯(上)
回溯算法三部曲
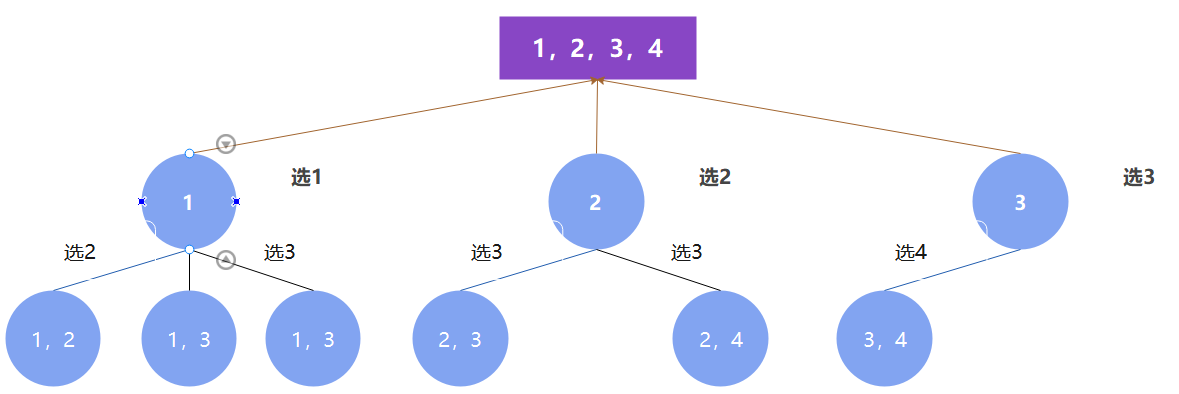
- 以LeetCode77.组合为例:
递归函数的返回值以及参数
定义两个全局变量,一个用来存放符合条件的结果的集合,一个用来存放单一结果。
1 | List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();// 存放符合条件结果的集合 |
递归函数终止条件
本题需要返回范围 [1, n] 中所有可能的 k 个数的组合,不难得出终止条件的代码如下:
1 | if (tmp.size() == k) { |
单层搜索的过程
本题的重点是需要一个int型的变量start来记录本层递归中集合从哪里开始遍历。
遍历过程如图所示,start主要起剪枝作用。
1 | for (int i = start; i <= n; i++) { // 控制树的横向遍历 |
tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);为回溯的操作,移除上一轮递归的结果,开始下一轮递归。
完整代码如下:
1 | class Solution { |
组合问题
LeetCode 77. 组合
LeetCode题目链接
在上面的回溯算法三部曲中已经详细解释了其过程,这里不再过多赘述。
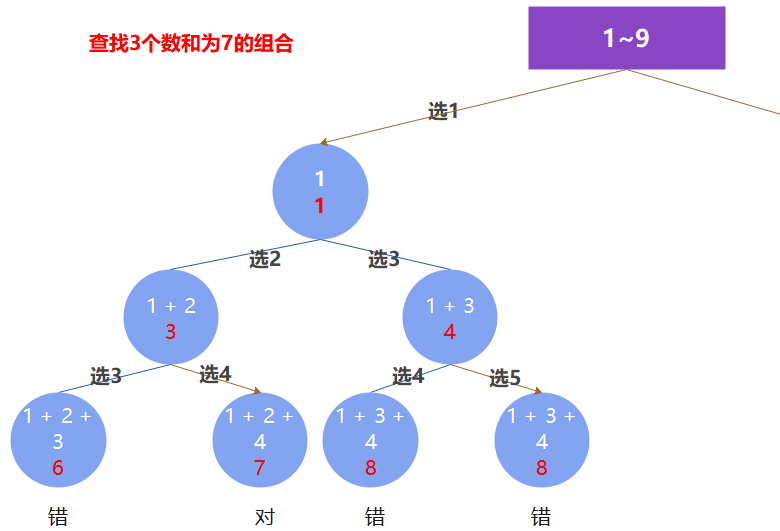
LeetCode 216. 组合总和 III
LeetCode题目链接
以先取1为例,不难画出其树形结构:
回溯三部曲:
确定回溯函数参数
1
2
3
4
5
6List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
int sum = 0;//记录每层递归的和
int count = 0;//记录收集了多少个数
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3(int k, int n)显然此题答案存在于叶子节点,题中需要的数字个数 k 正好是树需要遍历的深度,我们不妨定义一个
int型的变量 count 来记录树深,同时定义一个int型变量 sum 记录和,那么终止条件自然就得到了。确定终止条件
1
2
3if(count == k && sum == n){
res.add(new ArrayList(tmp));
}确定单层遍历逻辑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10for (int i = start; i <= 9; i++) {
//每次循环更新sum和count,同时把当前数放入tmp中,回溯过程镜像此操作。
sum += i;
count++;
tmp.add(i);
backtrack(k, n, i + 1);
sum -= i;
count--;
tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);
}本题也需要一个 start 来记录本层递归中集合从哪里开始遍历。同是 start 也可以代替 count 起到剪枝的作用,用 count 的好处是代码更具有可读性。
完整代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
int sum = 0;//记录每层递归的和
int count = 0;//记录收集了多少个数
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) {
if (n == 0 || k == 0) {
return res;
}
backtrack(k, n, 1);
return res;
}
private void backtrack(int k, int n, int start) {
if (count == k && sum == n) {
res.add(new ArrayList(tmp));
}
//剪枝
if (count > k || sum > n) {
return;
}
for (int i = start; i <= 9; i++) {
sum += i;
count++;
tmp.add(i);
backtrack(k, n, i + 1);
sum -= i;
count--;
tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);
}
}
}
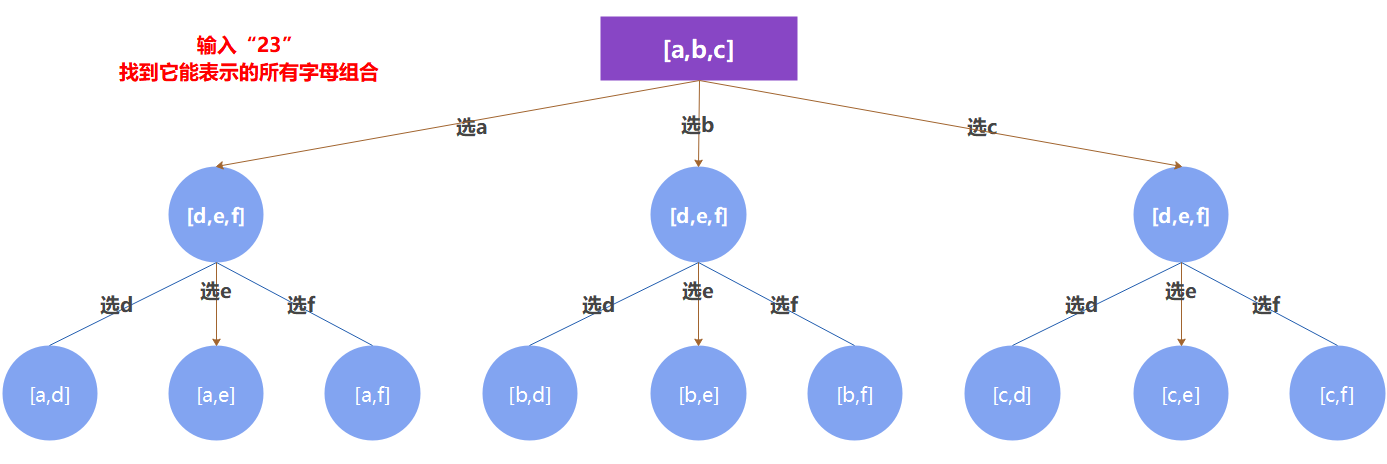
LeetCode 17. 电话号码的字母组合
LeetCode题目链接
前两道题都是求同一集合中的不同组合,而这道题是在不同的集合中求不同的组合。
树状图
回溯三部曲:确定回溯函数参数
1
2
3
4List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
StringBuilder tmp = new StringBuilder();//多次对字符串切割,故使用StringBuilder比String效率高很多
private void backtrack(String digits, String[] numString, int num)确定终止条件
1
2
3
4if(num == digits.length()){
res.add(tmp.toString());
return;
}确定单层遍历逻辑
1
2
3
4
5
6//因为是求不同集合中的组合,所以i不再从start开始
for(int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++){
tmp.append(str.charAt(i));
backtrack(digits, numString, num + 1);
tmp.deleteCharAt(tmp.length() - 1);
}完整代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28class Solution {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
StringBuilder tmp = new StringBuilder();
public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) {
if (digits == null || digits.length() == 0) {
return res;
}
//0 和 1 不记录,用""占位处理异常情况
String[] numString = {"", "", "abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz"};
backtrack(digits, numString, 0);
return res;
}
private void backtrack(String digits, String[] numString, int num) {
if (num == digits.length()) {
res.add(tmp.toString());
return;
}
String str = numString[digits.charAt(num) - '0'];//str 表示当前num对应的字符串
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
tmp.append(str.charAt(i));
backtrack(digits, numString, num + 1);
tmp.deleteCharAt(tmp.length() - 1);
}
}
}
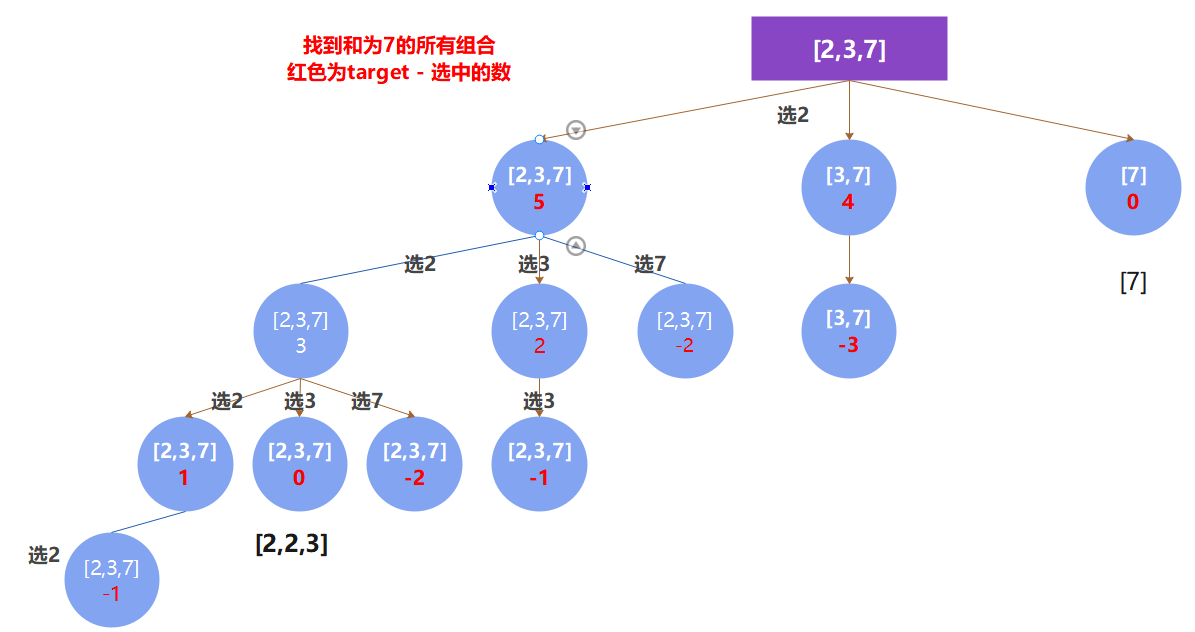
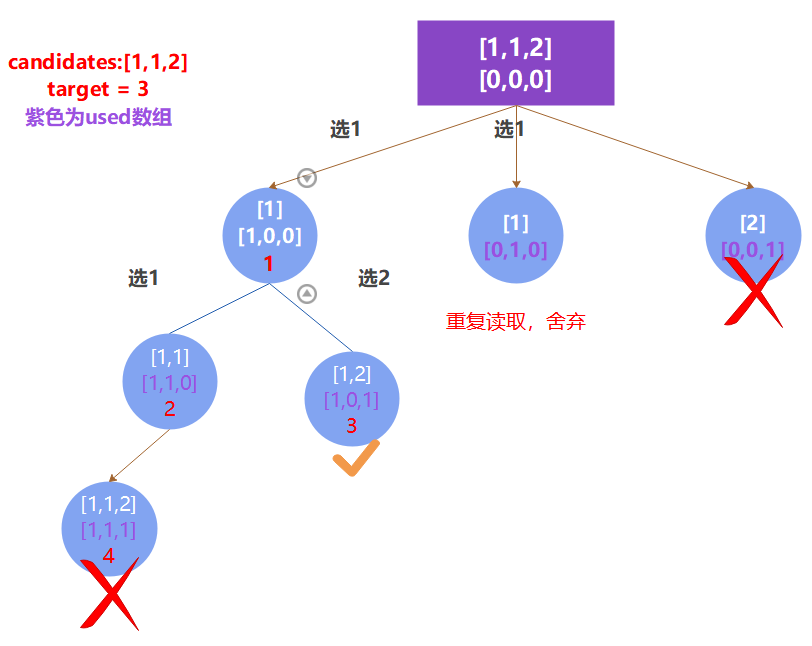
LeetCode 39. 组合总和
LeetCode题目链接
在77.组合和216.组合总和III中都要递归k层,因为要选取k个元素。而本题不限制元素个数,所以当选取的元素和大于 target 时就立即返回。
- 树状图
图中可以清晰的看到,纵向递归是可以取到重复元素的,而横向则不可以,这样避免了得到[2,2,3]和[2,3,2]这样的重复结果。
而达到这个目的的关键因素就是我定义的start。
回溯三部曲:
确定回溯函数参数
1
2
3
4List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
//一个集合求组合,需要用start控制遍历起点
private void backtrack(int[] candidates, int target, int start)确定终止条件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8//和已经大于target
if(target < 0){
return;
}
if(target == 0){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));
return;
}确定单层遍历逻辑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9for(int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++){
//如果和大于target,剪枝
if(target < 0){
break;
}
tmp.add(candidates[i]);
backtrack(candidates, target - candidates[i], i);
tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);
}完整代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates);
backtrack(candidates, target, 0);
return res;
}
private void backtrack(int[] candidates, int target, int start) {
//和已经大于target
if (target < 0) {
return;
}
if (target == 0) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (target < 0) {
break;
}
tmp.add(candidates[i]);
backtrack(candidates, target - candidates[i], i);
tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);
}
}
}
LeetCode 40. 组合总和 II
LeetCode题目链接
这道题与39. 组合总和最大的不同是集合中的元素不可以重复使用,所以需要定义一个布尔型的数组来告诉程序哪些元素已经在本轮递归中使用过。
回溯三部曲:
确定回溯函数参数
1
2
3
4
5
6List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
int sum = 0; //记录各元素之和,也可以跟上题一样使用target - candidates[i]
boolean[] used;
private void backtrack(int[] candidates, int target, int start)确定终止条件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7//剪枝
if(sum < 0 || sum > target){
return;
}
if(sum == target){
res.add(new ArrayList(tmp));
}单层递归逻辑
本题难点在于 数组candidates 有重复元素,但还不能有重复的组合,即如何去重。
为了将重复的数字都放到一起,所以先进行排序。
由树状图可以看出,当同一层的前一个元素等于当前元素且前一个元素没有被访问过的时候,就要做去重操作。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18for(int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++){
/**
!used[i - 1]代表数层去重,前一个还没访问过
例如[1,1,6],此时used为[0,1,0]
*/
if(i > 0 && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1] && !used[i - 1]){
continue;
}
sum += candidates[i];
used[i] = true;
tmp.add(candidates[i]);
backtrack(candidates, target, i + 1);
sum -= candidates[i];
used[i] = false;
tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);
}完整代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
int sum = 0;
boolean[] used;
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
if (candidates.length == 0) {
return res;
}
used = new boolean[candidates.length];
// 加标志数组,用来辅助判断同层节点是否已经遍历
Arrays.fill(used, false);
//对原始数组排序,将重复元素放在一起
Arrays.sort(candidates);
backtrack(candidates, target, 0);
return res;
}
private void backtrack(int[] candidates, int target, int start) {
if (sum < 0 || sum > target) {
return;
}
if (sum == target) {
res.add(new ArrayList(tmp));
}
for (int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) {
/**
!used[i - 1]代表数层去重,前一个还没访问过
例如[1,1,6],此时used为[0,1,0]
*/
if (i > 0 && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1] && !used[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
sum += candidates[i];
used[i] = true;
tmp.add(candidates[i]);
// 每个节点仅能选择一次,所以从下一位开始
backtrack(candidates, target, i + 1);
sum -= candidates[i];
used[i] = false;
tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);
}
}
}
分割问题
LeetCode 131. 分割回文串
LeetCode题目链接
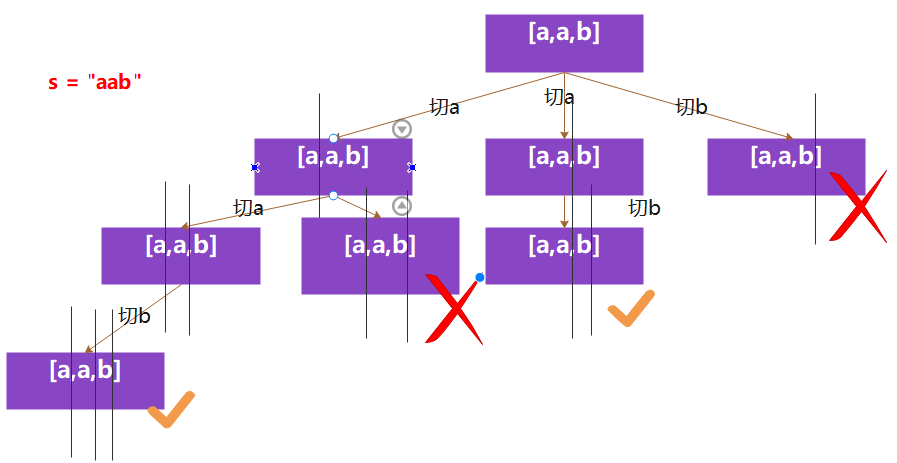
切割问题本质上类似于组合问题。
以[a,a,b]举例:
在组合问题中,第一个 a 递归完毕,就该拿出第二个a再跑一遍。
在切割问题中,第一段 a 切割完毕,就该拿出第二段 aa 再进行切割。
结合树状图会看的更清晰:
当切割线走到数组结尾时,正好切割完毕。
回溯三部曲:
确定回溯函数参数
1
2
3
4List<String> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>();
//start相当于切割线
private void backtrack(String s, int start)确定终止条件
1
2
3
4if(start >= s.length()){
res.add(new ArrayList(tmp));
return;
}确定单层循环逻辑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20for(int i = start; i < s.length(); i++){
if(isTrue(s, start, i)){
String str = s.substring(start, i + 1);
tmp.add(str);
}else{
continue;
}
backtrack(s, i + 1);
tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);
}
//判断回文
private boolean isTrue(String s, int start, int end){
for(int l = start, r = end; l < r; l++, r--){
if(s.charAt(l) != s.charAt(r)){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}完整代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35class Solution {
List<String> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
backtrack(s, 0);
return res;
}
private void backtrack(String s, int start) {
if (start >= s.length()) {
res.add(new ArrayList(tmp));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (isTrue(s, start, i)) {
String str = s.substring(start, i + 1);
tmp.add(str);
} else {
continue;
}
backtrack(s, i + 1);
tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);
}
}
private boolean isTrue(String s, int start, int end) {
for (int l = start, r = end; l < r; l++, r--) {
if (s.charAt(l) != s.charAt(r)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
LeetCode 93.复原IP地址
LeetCode题目链接
本题与131. 分割回文串类似,只需要把所有可能性搜索出来即可。
树状图也与上题一样,start在充当切割线的同时避免取到重复元素。
回溯三部曲:
确定回溯函数参数
1
2
3List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
//这种对字符串做频繁修改的题目建议用StringBuilder,我这样做不但复杂而且效率低。
private void backtrack(String s, int start, int pointSum)确定终止条件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7//12位的IP地址由三个逗点隔开,所以当 pointNum = 3时将集合加入结果集中
if(pointSum == 3){
if(isLegal(s, start, s.length() - 1)){
res.add(s);
}
return;
}确定单层循环逻辑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33for(int i = start; i < s.length(); i++){
if(isLegal(s, start, i)){
s = s.substring(0, i + 1) + "." + s.substring(i + 1);
pointSum++;
backtrack(s, i + 2, pointSum);
s = s.substring(0, i + 1) + s.substring(i + 2);
pointSum--;
}
}
//判断一段ip是否合法
private boolean isLegal(String s, int start, int end){
if(start > end){
return false;
}
//以0开头不合法
if(s.charAt(start) == '0' && start != end){
return false;
}
int sum = 0;
for(int i = start; i <= end; i++){
//遇到非数字不合法
if(s.charAt(i) > '9' || s.charAt(i) < '0'){
return false;
}
sum = sum * 10 + (s.charAt(i) - '0');
//此段IP大于255不合法
if(sum > 255){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
完整代码
1 | class Solution { |